Hackers are stealing your crypto
Heyo,
Jules here, from Cyfrin.
6%+ of all assets in crypto were stolen last year due to security breaches.
This means there's a 1 in 20 chance all your money in DeFi will be gone in a year.
Here’s how hackers are stealing your crypto in 2023
Top 5 attack vectors today
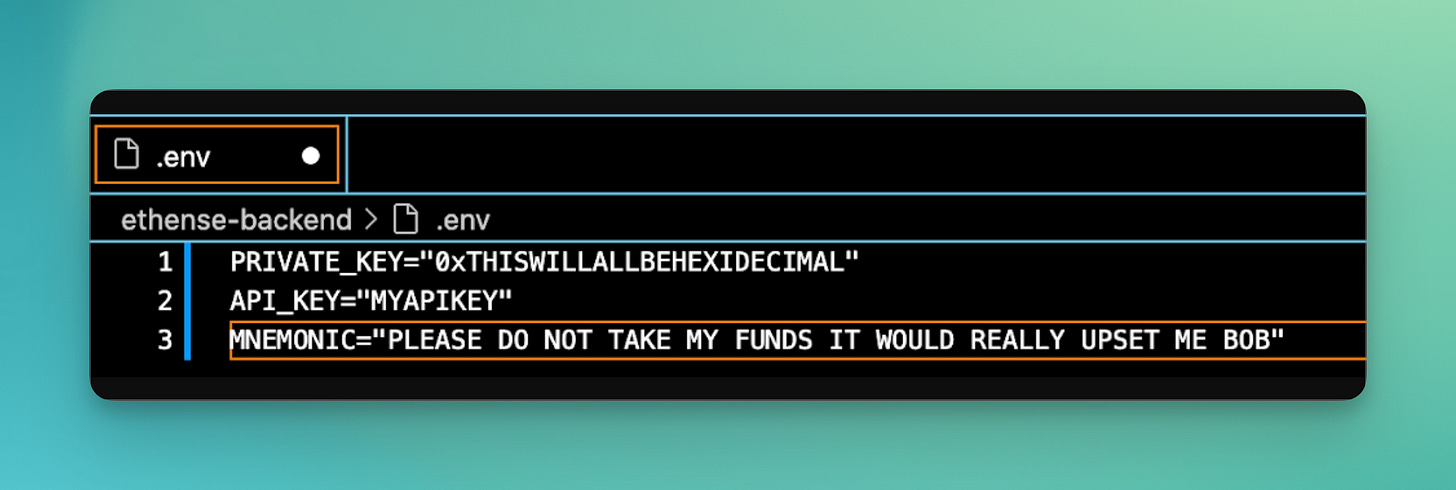
1. 🗝️ Stolen private keys [$243M stolen through 16 attacks]
As devs, we often need to add our private keys in files in order to interact with smart contracts. However, if we forget and deploy keys to the public, any contract we’ve deployed is now in danger of potentially loosing of millions of dollars to attackers.
— How to spot: usually private keys are found within .env files, shared company docs, or previous repository versions.
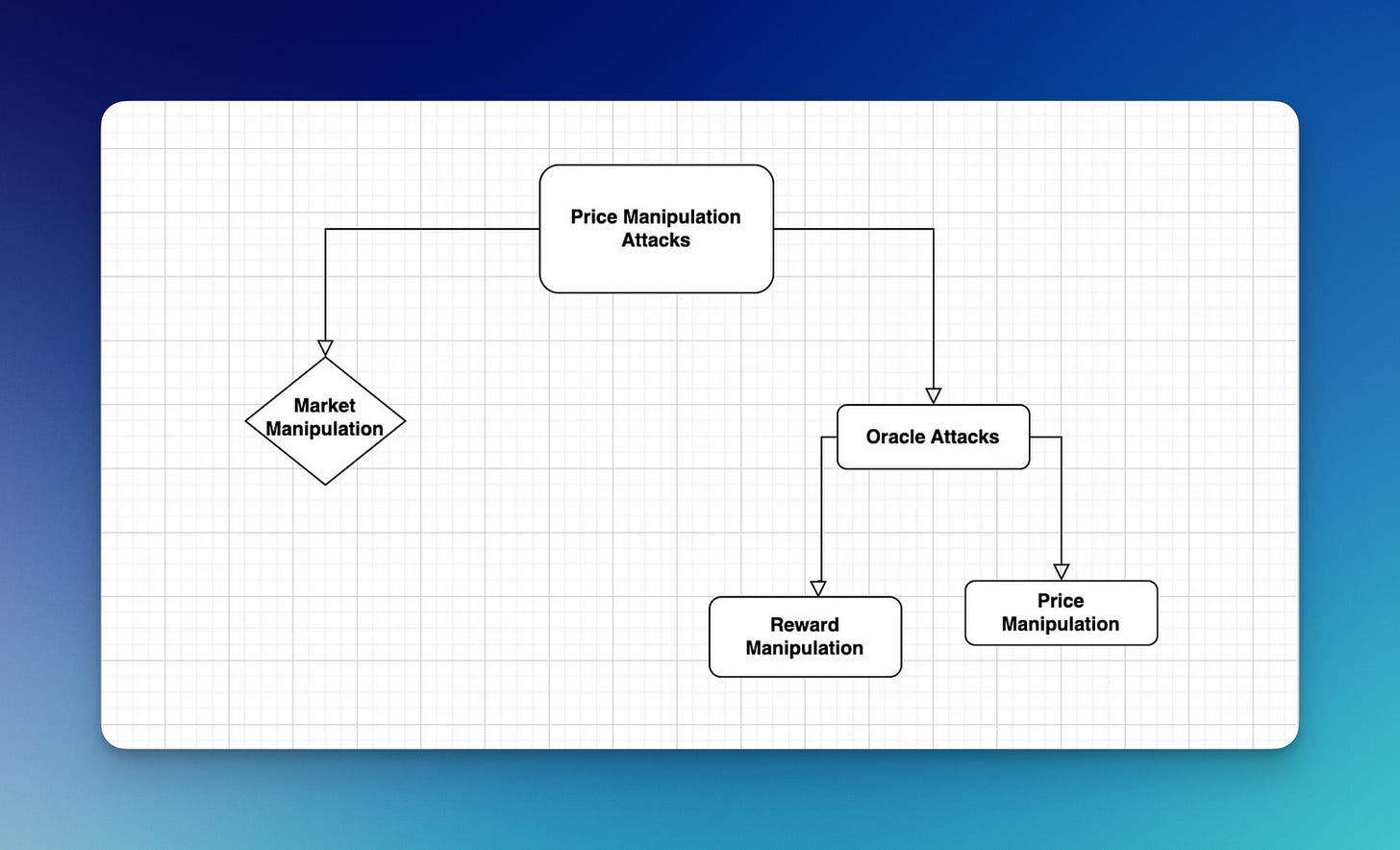
2. 💰 Reward manipulations [$200M stolen through 27 attacks]
Reward manipulation attacks are like price oracle manipulations, except they manipulate the rewards or incentives provided by a system.
— How to spot: malicious actors artificially influence the rewards or incentives built into smart contracts, through front-running (with insider information or MEV) or through wash trading (pump and dump scheme to give the impression of a higher trade volume in order to attract legitimate traders to the market).
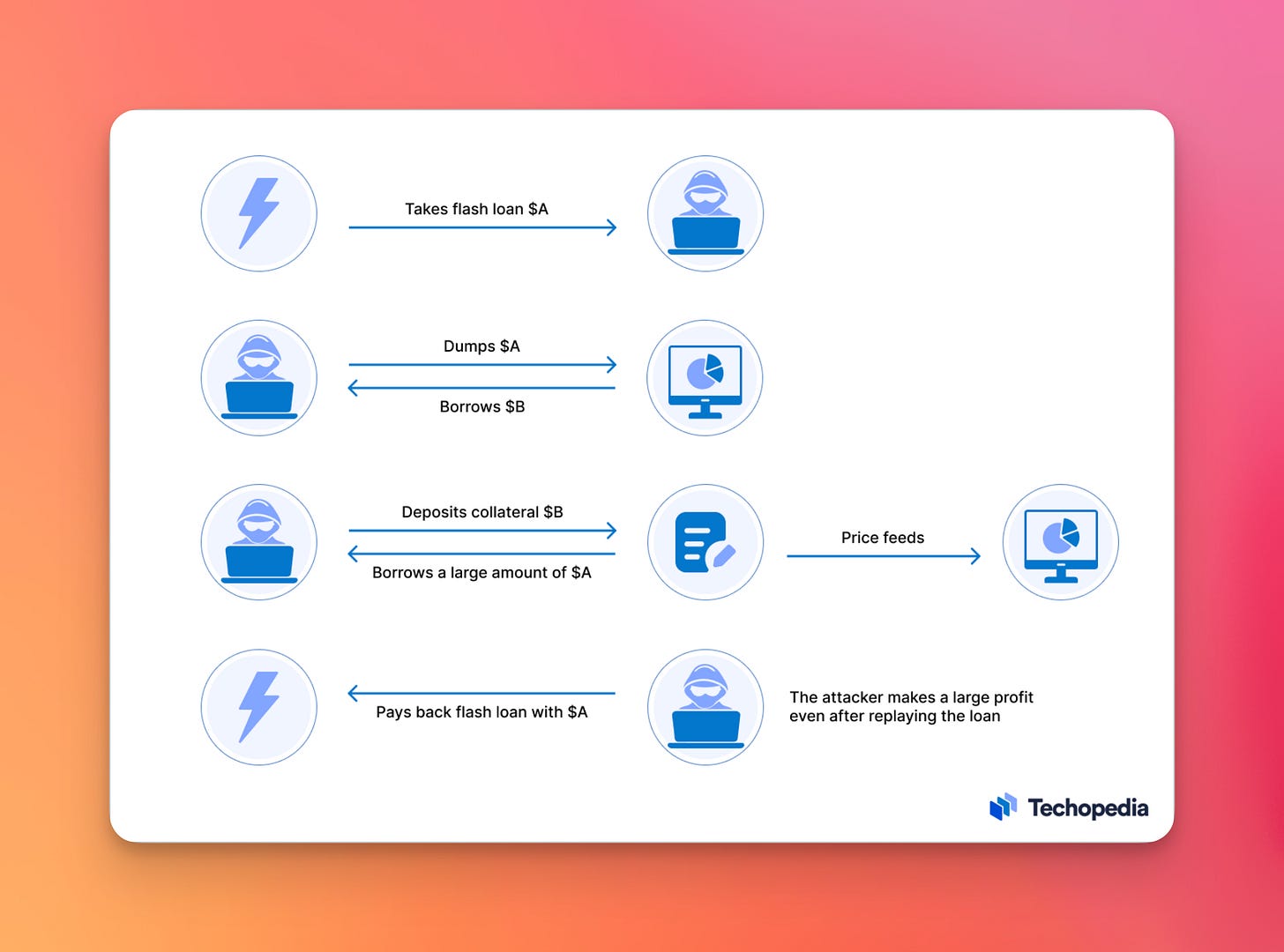
3. 💵 Price oracle manipulations [$146M stolen through 52 attacks]
Price oracle manipulations happen when an oracle’s price feed is manipulated, ultimately impacting behavior within DeFi protocols and enabling arbitrage opportunities.
— How to spot: attackers usually leverage Flash Loans to manipulate the price of assets in automated market makers, like Uniswap, to change the spot price of a token before the lender smart contract looks up the token again.
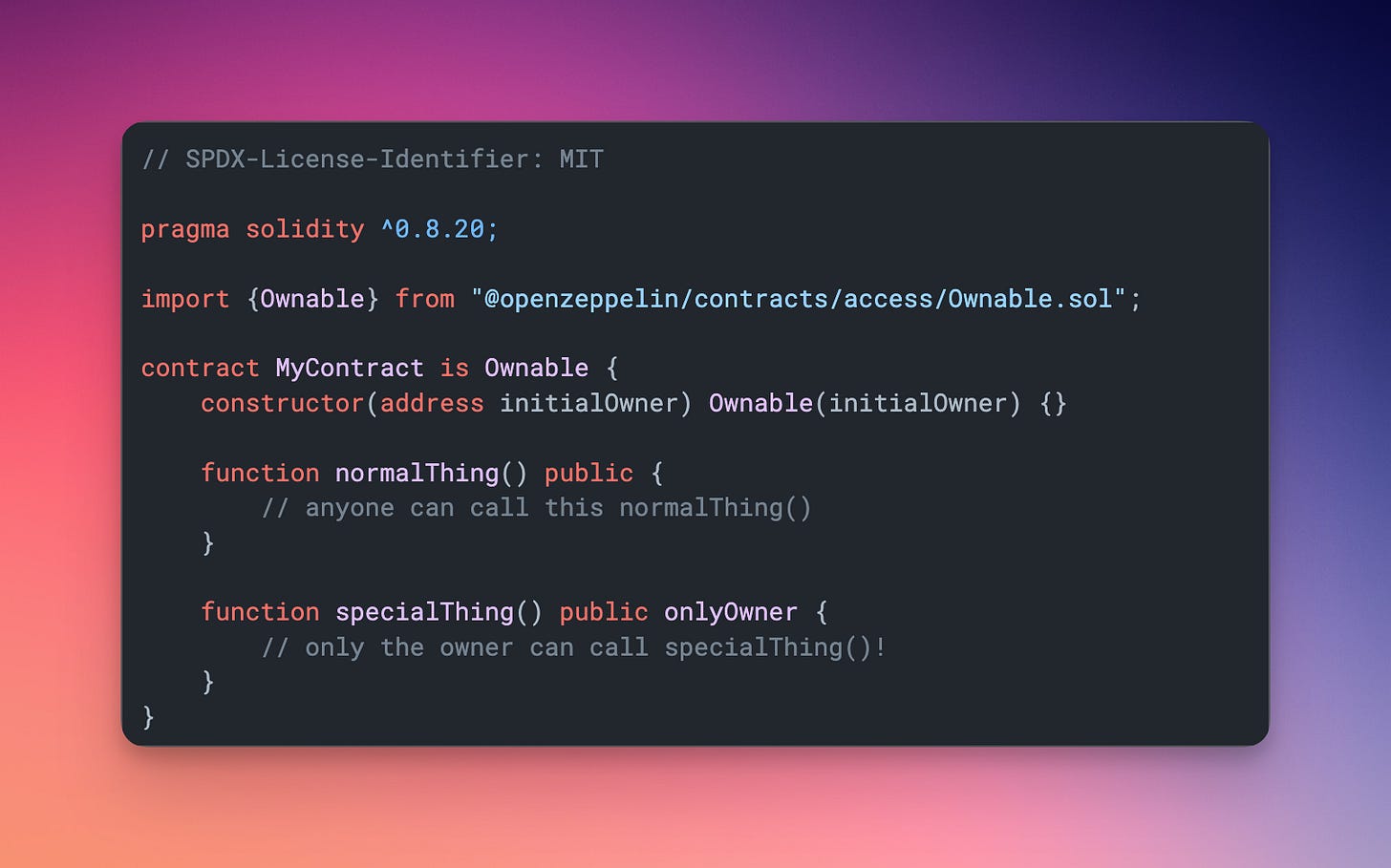
4. 🔐 Insufficient function access control [$17M stolen through 25 attacks]
Some functions can be accessed by everyone, others only by specific addresses.
Mistakes in function access control, like enabling a function to be public which should be set to private, open the door for hackers to intercept actions they shouldn’t have access to.
— How to spot: look for the modifiers within a function to see who is able to access a function. Always question why someone has access to a function and whether that’s entirely necessary for the protocol to function.
5. ♻️ Logic error [$17M stolen through 9 attacks]
Sometimes the code doesn’t do exactly what you programmed it to do. Logic errors attack code that is well written, but somehow does something different than what the developers expected it to do.
— How to spot: found in inconsistencies between the documentation and how the code behaves. Reading comments, developer docs, and testing our behaviors is how we spot these.

At Cyfrin, we’ve been reviewing these attacks ourselves both through our private and competitive audits.
To get an glimpse at how these vulnerabilities are exploited in real life, check out our case studies - the latest one focusing on governance attacks.
Keeping up with Web3 security
Vulnerability found within ThirdWeb in a commonly used open-source library in the web3 industry - not yet exploited.
Coinbase rolls out money transfers via links sent on WhatsApp, TikTok and Instagram.
Seattle judge accepts former Binance CEO Changpeng Zhao's guilty plea.
Always feel free to reach out if there’s anything we can support or collaborate on.
Sending lots of cyber love,
Jules 🤸🏻